What is design thinking?
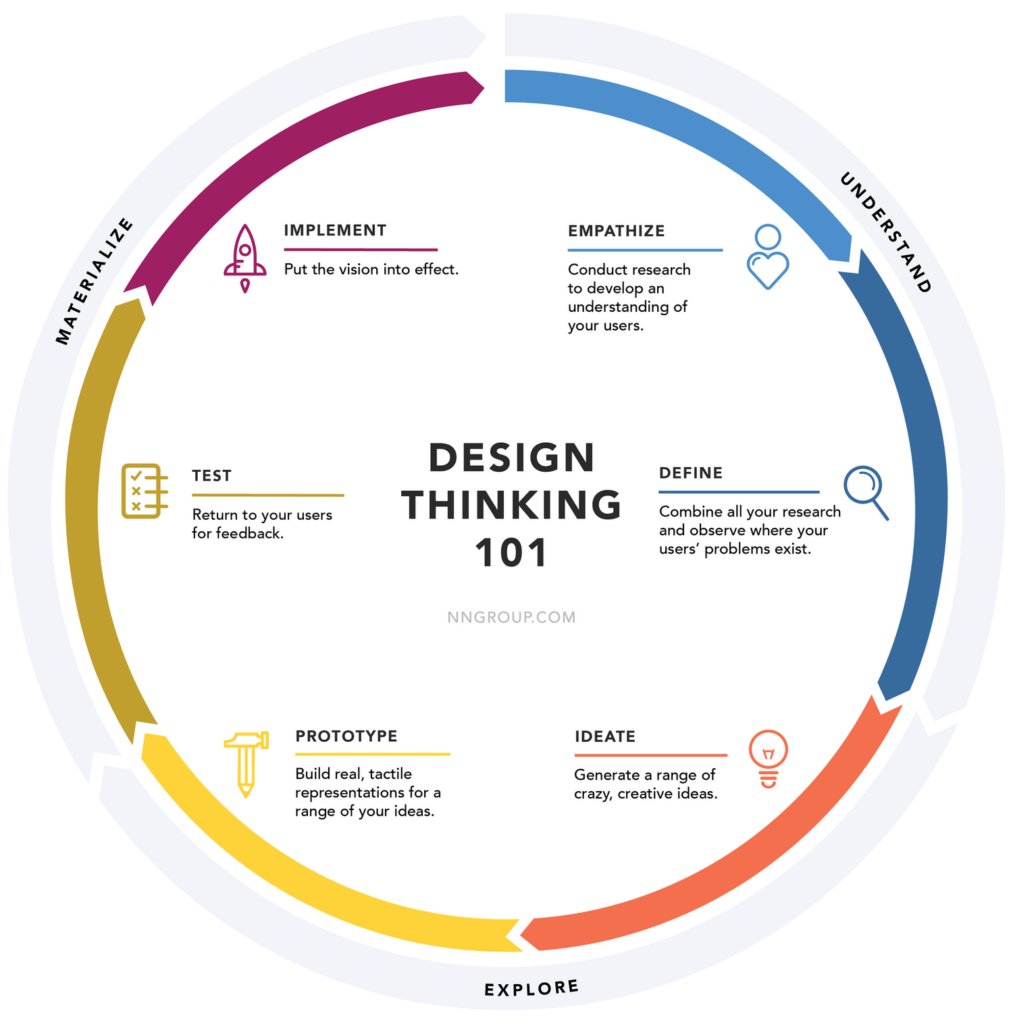
Design thinking is a human-centered approach to problem-solving and creativity. The strategy seeks to place users first, by understanding their problems and circumstances, to provide a better user experience. The approach seeks to challenge vague assumptions through actual research, conceptualising solutions that can be tested and iterated.
The design thinking process consists of 5 main stages: empathise, define, ideate, prototype, and test. The framework generally starts with first understanding the user’s needs and identifying challenges they face through conducting user interviews, surveys, or ethnographic research. The research results are then used to craft problem statements and identify potential opportunities, which would be addressed in the ideation and testing stage. These few stages of the design thinking process are highly iterative as ideas and prototypes are continually designed, tested, and refined before actual implementation.